The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has developed a comprehensive suite of tools for accessing, managing, analyzing and sharing building energy data. Tools like Audit Template, SEED and UBID are being used by jurisdictions to support BPS data collection, reporting, standardization, management, and compliance as described below
- Audit Template is a web-based tool that can be used to collect building system and energy audit information in a standardized format. In the context of BPS, this tool can be used by both cities and building owners as part of alternative compliance pathways that require an energy audit or other building-level information reporting.
- The Standard Energy Efficiency Data (SEED) Platform is a central database that merges information from Energy Star Portfolio Manager (ESPM), Audit Template, and other datasets in one place. It can be used by jurisdictions for tracking the compliance status of all covered buildings in a BPS.
- Unique Building Identifier (UBID) is a technology that converts two-dimensional building footprint data into unique alphanumeric codes using an open-source grid reference system. It can be used by jurisdictions to create unique identifiers for buildings that can be standardized and shared across different databases, such as tax assessor data, benchmarking data, BPS compliance, and others.
The map below shows the adoption of these tools in U.S. jurisdictions that have adopted a benchmarking or BPS policy.
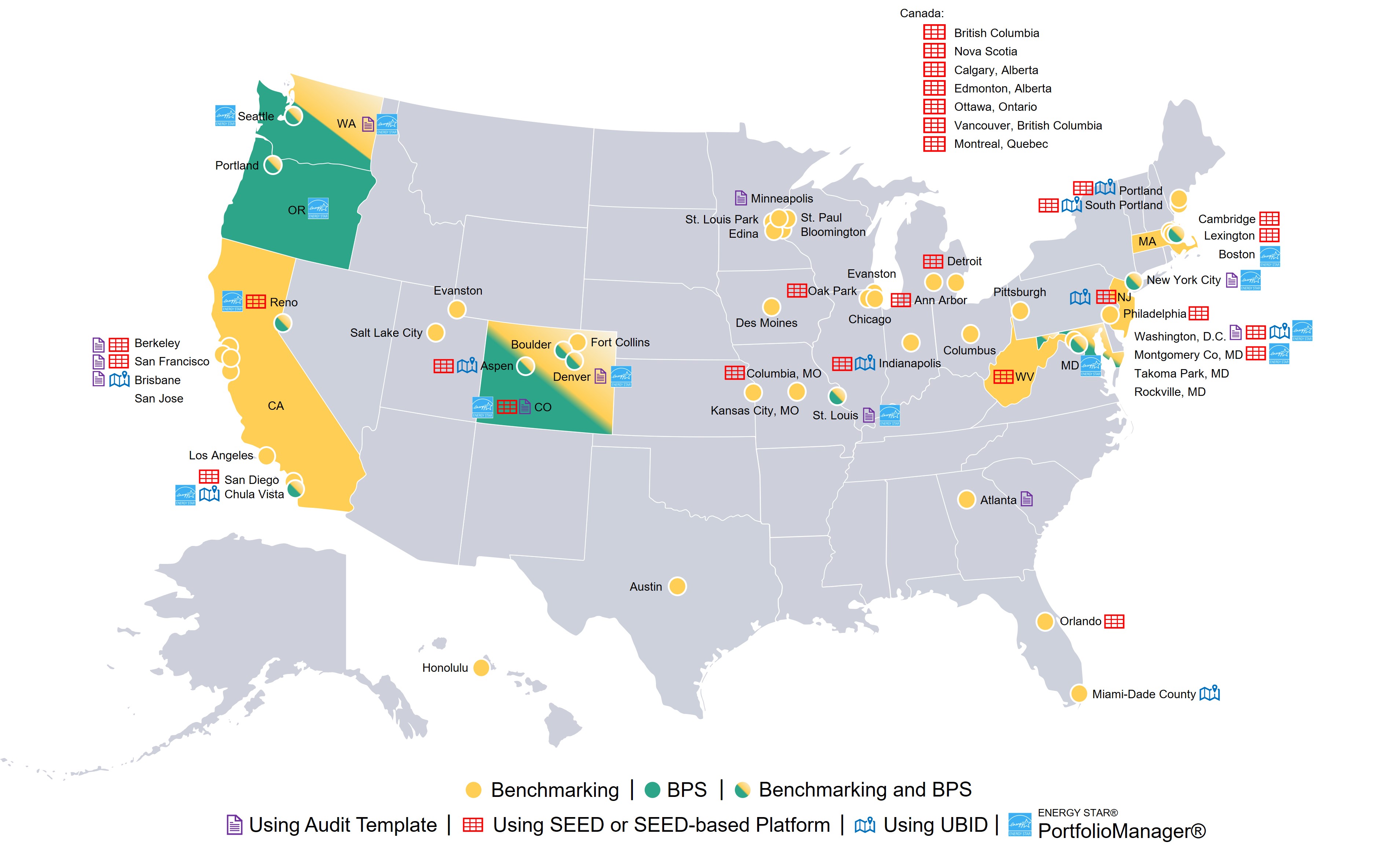
Other tools like Building Efficiency Targeting Tool for Energy Retrofits (BETTER) can also support BPS implementation by identifying cost-saving energy reductions in buildings and portfolios without site visits or complex modeling. For the full list of DOE tool descriptions and uses see the Building Data Tools site.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also developed tools that are being used to support BPS. For example, jurisdictions in the U.S. and Canada use EPA's ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager® to collect energy use and other performance metrics, building characteristics data, and more from buildings required to comply with BPS and other requirements. This web-based tool is free to use for building owners and policy administrators alike, serving as a central hub that takes in data from third party software and utility systems into building owner accounts, offers simple processes for building owners to report to jurisdictions, and allows jurisdictions to export reported information and metrics to platforms they use for further managing a policy.
